13.10/2023
POLEMA presented at the“BIOTECHMED” its innovative medical products
11.07/2023
POLEMA at INNOPROM in Ekaterinburg
Molybdenum rods, forged products
Rods of the following brands are produced:
- Mo-PM molybdenum rods and forged products;
- Mo99.95-PM super-thin molybdenum rods.
Application
Mo-PM and Mo99.95-PM rods and forged products are used to make components of high-temperature vacuum and hydrogen furnaces, hot zones of sapphire smelting units, components of gas turbines, heat exchangers, eletrodes for smelting glas and basalt, etc. The thermionic properties of molybdenum are as follows: electronic work function of 4.29 eV, low vacuum evaporation speed and vapor pressure at 1000-2000 оС, allowing the metal to be used widely in various structures of electrovacuum devices and as thermoelectric energy converters. Pure unalloyed molybdenum prepared using the method of PM-Mo powder metallurgy (POLEMA analogues include Mo-PM, Mo99.95-PM) is marked by good plastic characteristics after annealment for internal stress removal (ISR). The fraility threshold of Tx is in a temperature range well below room temperature. The σв РМ durability of ISR molybdenum in the range of high temperatures drops monotonically: 95-100 Mpa at T=1200 0С, 75-80 MPa at T=1400 0С, and approximately 50-40 Mpa at T=1600 -1800 0С. The useful life of molybdenum products is affected by the metal's creep and vaporization in a vacuum. The speed of molybdenum's vaporization is 2.07·10-9 g/cm2·sec at Т=1727 0С; 7.3·10-8 g/cm2·sec at Т=1927 0С; 5.03·10-6 g/cm2·sec at Т=2227 0С. Nevertheless, in structures operating in static conditions (screens of vacuum furnaces)—sheets and rods made of molybdenum M-MP and M99.95MP that are used, for example, to outfit hot zones for growing sapphire monocrystals—function under working temperatures of 2000 -2100 0С.
The temperatures of recrystallization of molybdenum are as follows: initiation at 900 0С, with full recrystallization commencing at 1100 0С (annealment within 1 hr). Once recrystallized, molybdenum is fragile at room temperature. In open air, molydbenum begins to oxidize at Т=400 0С, while the speed of oxidation accelerates significantly at Т > 600 0С.
These properties of pure unalloyed molybdenum determine the sphere of its application as a heat-resistant material.
1. Mo-PM molybdenum rods and forged products
Chemical composition
Current powder metallurgy methods ensure a high level of purity of molybdenum in terms of metallic interstitial impurities (C, N, O, H), the necessary microstructure for use as a heat-resistant construction material in electronics and other devices functioning in extremely high temperatures. The chemical composition of rods and forged products is ensured to meet or surpass the norms set for pristine molybdenum powder. Since 2002, the company has primarily used Mo powder 99,95 molydbenum powder in its products.
By virtue of its low concent of interstitial impurities and metallic impurities, as well as its small-grain structure, finished products are distinguished by outstanding plastic characteristics.
Guaranteed chemical composition of Mo powder 99.95 ТУ14-22-160-2002
| Brand | Мо, % minimum* | Chemical composition, ppm, maximum | ||||||||||||
| Fe | Al | Ni | Si | Mg | Na | K | Ca | W | Mn | Zn | C | ∑Ме** | ||
| Mo powder 99.95 | 99,95 | 100 | 30 | 50 | 50 | 20 | 30 | 80 | 40 | 130 | 10 | 5 | 40 | 500 |
*The weight percentage of Mo in Mo powder 99.95 is determined by subtracting the sum of all metallic admixtures controlled for using mass-spectrometry with ICP-MS inductively coupled plasma.
The gas-forming admixtures C, O, N, H, S, F, and Cl are not included when calculating the share of molybdenum.
** ∑Ме – total metallic admixtures
Dimensions of Mo-PM rods and forged products
Hot-rolled rods are produced with diameters of between 10 to 40 mm, and forged products (forged rods, cylinders, cubes, parallelipeds and sheets with a diameter or rectangular edge of 30-300mm to 1500 mm in length with a surface cleansed from oxides or tooled.
Annealment
At the client's request, products are manufactured with annealment for internal stress removal.
Tooling
At the client's request, rods and forged products are delivered with ground, turned or milled (for flat forged products) surfaces, whose dimensions and allowances are determined by the consumer's plans or order.
Microstructure
Microstructure is controlled in rods with a diameter of 30 mm or less. A full recrystallization structure is not permitted, unless otherwise requested by the client.
Guaranteed mechanical properties of hot-rolled rods Mo-PM
| Diameter, mm | Durability σ в, Н/mm2 (kgf/mm2) | Relative elongation, δ % |
| Minimum | ||
| 14,5-29 | 640 (65) | 20 |
| 30-40 | 590 (60) | 15 |
Upon agreement with the client, rods are delivered without any set mechanical properties with a guarantee that they meet the parameters established by the standard.
2. Precision-cut Mo99.95-PM molybdenum rods
Guaranteed chemical composition
| Brand |
Mo, %, minimum* |
Admixtures, ppm, maximum | ||||||||||||
| O | N | C | Fe | Al | Ni | Si | Mg | Na | K | Ca | Na | W | ||
| Mo99.95-PM | 99,95 | 70 | 50 | 100 | 100 | 30 | 50 | 50 | 20 | 30 | 80 | 40 | 30 | 130 |
| Total content of metallic admixtures < 500 ppm | ||||||||||||||
* The weight percentage Mo is determined by subtracting from 100% the total content of metallic admixtures (without including gas-forming elements)
The share of molybdenum and the total content of metallic admxtures is guaranteed and is set according to the client's request.
Sample chemical composition of 20 mm diameter rods*
| Brand |
Mo, % |
Admixtures, ppm, maximum | ||||||||||||
| O | N | C | Fe | Al | Ni | Si | Mg | Na | K | Ca | Na | W | ||
| Mo99,95-PM | 99,97 | 70 | 20 | 25 | 35 | 1 | 8 | 6 | 0,3 | 2,5 | < 10 | 40 | 30 | 130 |
| Total admixture content 275 mcg/g not including H, C, N, O, F, P, S, Cl | ||||||||||||||
* The full analysis of the chemical composition is determined using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS).
Deformation method
Hot rolling, extrusion, forging or cobbing.
Shapes of rods and forged products
Round, rectangular, or other cuts.
Surface finish
Rods are produced chemically cleansed of oxides or machined: tooled or ground. Local defects (with the exception of cracks, backfins and blemishes) on the surface of oxide-cleansed rods that do not cause the rods to exceed the maximum dimensions are permitted.
Roughness requirements for tooled rods are set based on the client's requests. Unless otherwise requested, the roughness of tooled rods is set at Ra 2.5 maximum, and the roughness of ground rods at Ra 1.25 maximum.
Dimensions and allowances for dimensions of round Mo99.95-PM rods
| Type | Diameter, mm | Diameter allowances, mm | Ovality, mm, maximum |
| Ground | 3,18 -12,7 | ± 0,05 | - |
| > 12,7 | ± 0,08 | - | |
| Turned | > 6 -10 | ± 0,18 | - |
| > 10 -18 | ± 0,21 | - | |
| > 18 -30 | ± 0,26 | - | |
| > 30 -50 | ± 0,31 | - | |
| > 50 -80 | ± 0,37 | - | |
| > 80* | ± 0,44 | - | |
| Without tooling, cleansed of oxides | 3,18-7,14 | ±0,05 | 0,1 |
| >7,14-10,32 | +0,25/-0,13 | 0,2 | |
| >10,32-15,9 | +0,25/-0,13 | 0,3 | |
| >15,9-22,2 | +0,38/-0,13 | 0,38 | |
| >22,2-25,4 | +0,51/-0,13 | 0,38 | |
| >25,4-34,9 | +0,51/-0,25 | 0,46 | |
| >34,9-38,1 | +0,51/-0,38 | 0,51 | |
| >38,1-41,3 | +0,64/-0,38 | 0,51 | |
| >41,3-50,8 | +0,76/-0,51 | 0,64 | |
| >50,8-63,5 | ±0,81 | 0,64 | |
| >63,5-82,6 | ±0,81 | 0,69 | |
| >82,6-88,9 | ±1,14 | 1,02 |
* Maximum dimensions of turned rods with a diameter of more than 80 mm are determined based on agreement with the client.
Dimension intervals and maximum deviations of rod dimensions are set in accordance with the STM B 387 standard
Rod length is established in accordance with the client's request.
Length allowances are < ± 6.35 mm.
Curvature < 1.27 mm for 305 mm of length.
Acceptable deviations for rod dimensions of rectangular or other cuts other than round cuts are established based on client request.
Guaranteed mechanical properties of Mo99.95-PM rods
| Diameter, mm | Durability σ в, Н/mm2 | Relative elongation δ , % | Vickers hardness HV10 |
| Minimum | |||
| 3,18 –10,32 | 515 | 15 | Not specified |
| > 10,32 –22,2 | 620 | 18 | 230-280 |
| > 22,2 –28,6 | 585 | 15 | 225-270 |
| > 28,6 –47,6 | 515 | 10 | 215-260 |
| > 47,6 -73 | 480 | 10 | 210-250 |
| > 73 –88,9 | 450 | 10 | 205-240 |
Norms of mechanical properties are set for material following annealment at 900 0С over the course of 0.5 hrs.
Thermal treatment and microstructure
Rods are thermally treated, with annealment for internal stress removal, unless otherwise requested by the client.
In the microstructure of rods with a diameter of 40 mm or less, full recrystallization structure is not permitted, unless otherwise requested by the client, and special requests regarding recrystallization annealing or structure parameters are agreed to.
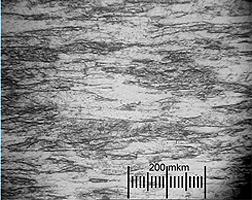
Sample structures and mechanical properties of Mo99,95-PM rods with a 20 mm diameter
Microstructure, transverse and end-on direction, x200
After annealing (for internal stress removal)
Average grain size is 20-30 microns.
Average grain size 20-30 mcm.
Hardness HV10 230 kgf/mm2
Short-term strength at room temperature σв 690 N/mm2
Relative elongation δ 33%.
Durability at 18000С σв 40 N/mm2, relative elongation δ 17%